Vba if Condition Continue Else Exit
Author: Oscar Cronquist Article last updated on February 07, 2022
This article demonstrates how to use the If ... Then statement in Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). You can combine the If ... Then statement with Else and ElseIf to make it more versatile and create more advanced conditions.
Table of Contents
- How to use the If ... Then statement (VBA)
- If ... Then condition: larger than
- If ... Then condition: equal to
- If ... Then condition: not equal to
- How to use the If ... Then ... End If statement (VBA)
- How to use the If Then Else Endif statement (VBA)
- How to use the If Then Elseif Else End if statement (VBA)
- Where to put the code?
- How to run a macro
- Get Excel *.xlsx file
1. How to use the If ... then statement

The picture above demonstrates an If ... Then statement using a condition, you can use logical operators like the:
- < less than sign
- > greater than sign
- = equal sign
- <> not equal signs meaning a smaller than and a larger than sign combined.
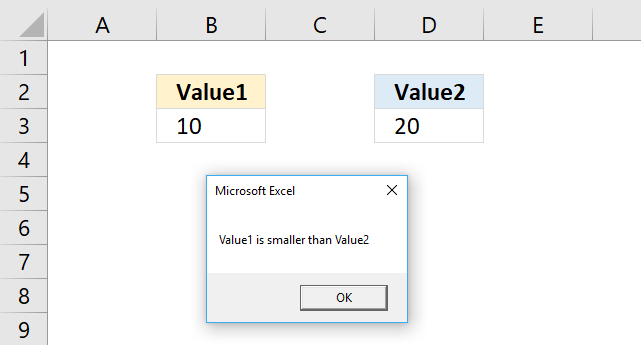
This particular example checks if the value in B3 is smaller than the value in cell D3. If true the If statement runs the remaining code after the Then statement, in this case, it shows a message box with text Value1 is smaller than Value2. See the image above.
VBA code
'Name macro Sub Macro1() 'If ... Then statement If Range("B3") < Range("D3") Then MsgBox "Value1 is smaller than Value2" 'Stop macro End Sub Where to put the code?
How to run a macro?
Back top
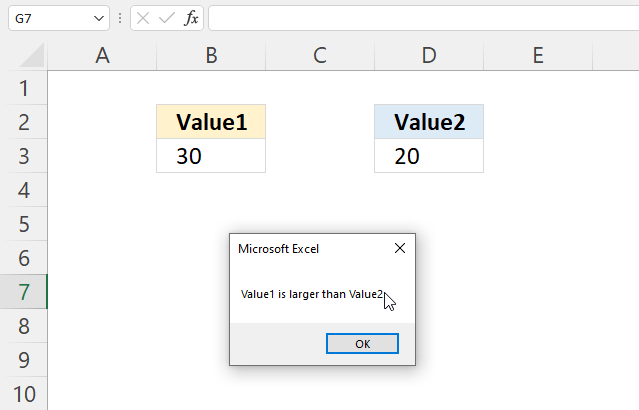
1.1 If ... Then condition: larger than
VBA code
'Name macro Sub Macro1() 'If ... Then statement If Range("B3") > Range("D3") Then MsgBox "Value1 is larger than Value2" 'Stop macro End Sub Where to put the code?
How to run a macro?
Back top
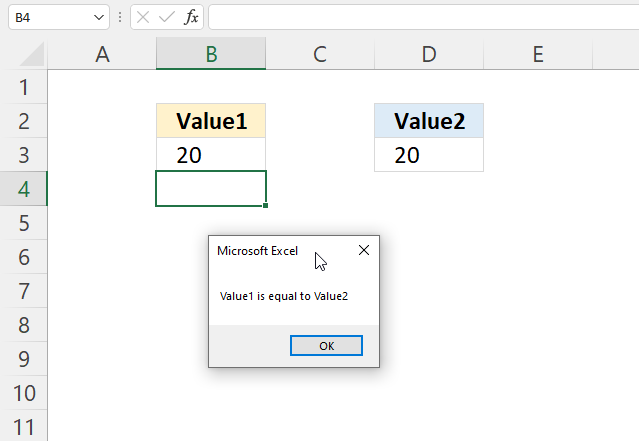
1.2 If ... Then condition: equal to
VBA code
'Name macro Sub Macro1() 'If ... Then statement If Range("B3") = Range("D3") Then MsgBox "Value1 is equal to Value2" 'Stop macro End Sub Where to put the code?
How to run a macro?
Back top
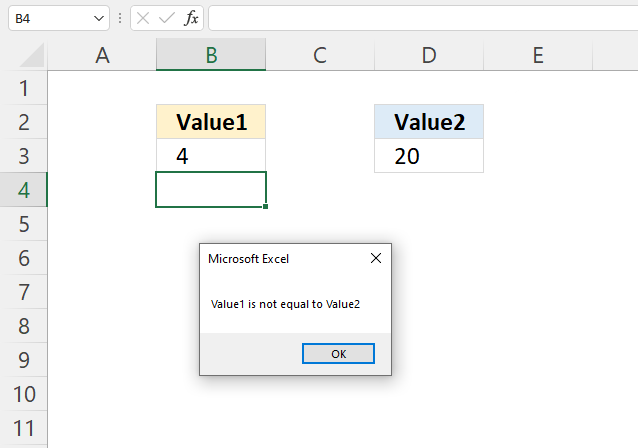
1.3 If ... Then condition: not equal to
VBA code
'Name macro Sub Macro1() 'If ... Then statement If Range("B3") <> Range("D3") Then MsgBox "Value1 is not equal to Value2" 'Stop macro End Sub Where to put the code?
How to run a macro?
Back to top
2. How to use the If ... Then ... End If statement
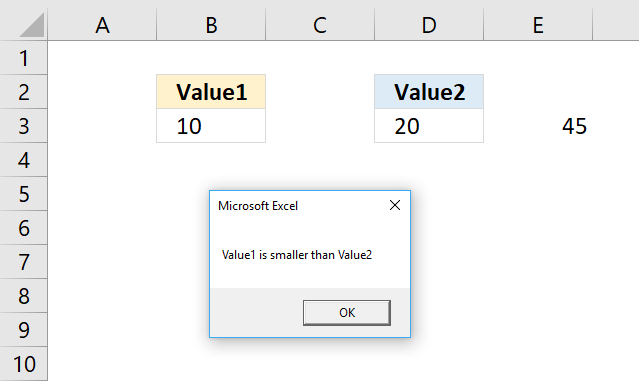
The If ... Then ... End If statement allows you to run multiple lines of code, the End if statement tells the subroutine when the lines have been run and the If ... Then ... End if statement is completed.
2.1 VBA code
'Name macro Sub Macro2() 'If ... Then ... Endif statement If Range("B3") < Range("D3") Then 'Save number 45 to cell E3 in current worksheet Range("E3") = 45 'Show message box MsgBox "Value1 is smaller than Value2" End if 'Stop macro End Sub The subroutine above saves the number 45 to cell E3 if the value in cell B3 is smaller than the value in D3.
The msgbox function then displays a dialog box containing the message Value1 is smaller than Value2.
Where to put the code?
How to run a macro?
Back to top
3. How to use the If ... Then ... Else ... End if statement
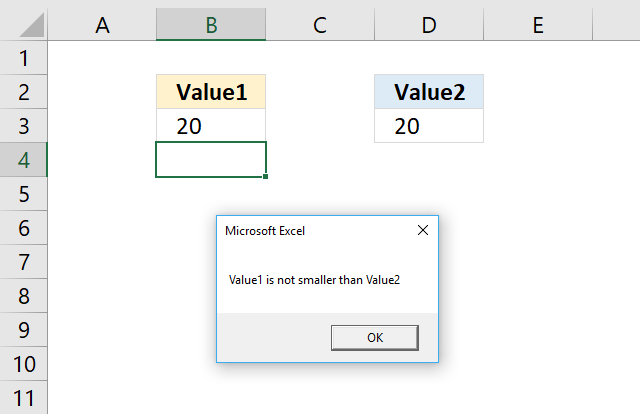
The ELSE statement allows you to run code if the logical expression is not met.
3.1 VBA code
'Name macro Sub Macro3() 'If ... Then ... Else ... Endif statement If Range("B3") < Range("D3") Then 'Display message box MsgBox "Value1 is smaller than Value2" Else 'Display message box MsgBox "Value1 is not smaller than Value2" End If 'Stop macro End Sub Where to put the code?
How to run a macro?
Back to top
4. How to use the If ... Then ... Elseif ... Else ... Endif statement
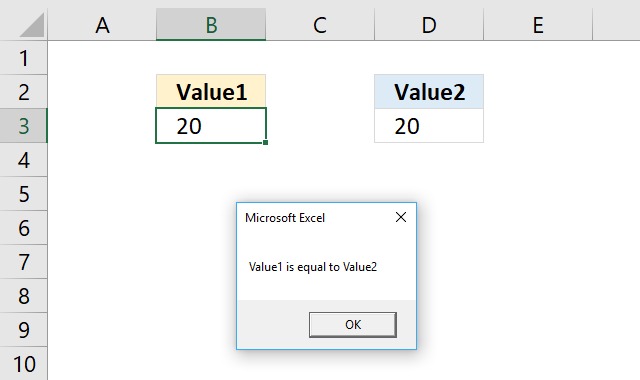
The ELSEIF statement lets you create another logical expression, you may have multiple ELSEIFs in the statement.
4.1 VBA code
'Name macro Sub Macro4() 'If ... Then ... ElseIf ... Else ... Endif statement If Range("B3") < Range("D3") Then 'Display message box MsgBox "Value1 is smaller than Value2" ElseIf Range("B3") = Range("D3") Then 'Display message box MsgBox "Value1 is equal to Value2" Else 'Display message box MsgBox "Value1 is larger than Value2" End If 'Stop macro End Sub Where to put the code?
How to run a macro?
Back to top
5. Where to put the VBA code?
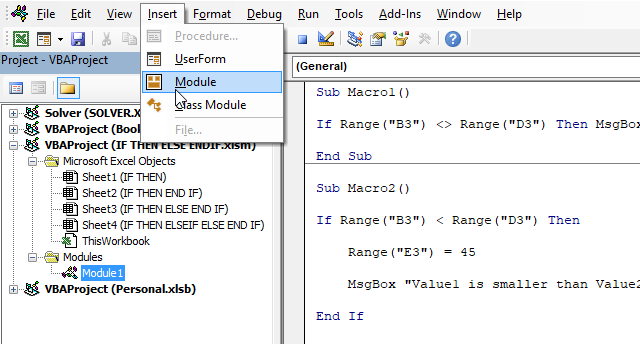
- Copy the VBA macro code.
- Press Alt and F11 to open the Visual Basic Editor (VBE).
- Press with left mouse button on "Insert" on the top menu.
- Press with left mouse button on "Module", see the image above.
- A new module is inserted, see the Project Explorer above.
- Paste the VBA macro code to the code module.
- Exit VBE and return to Excel.
6. How to run a VBA macro
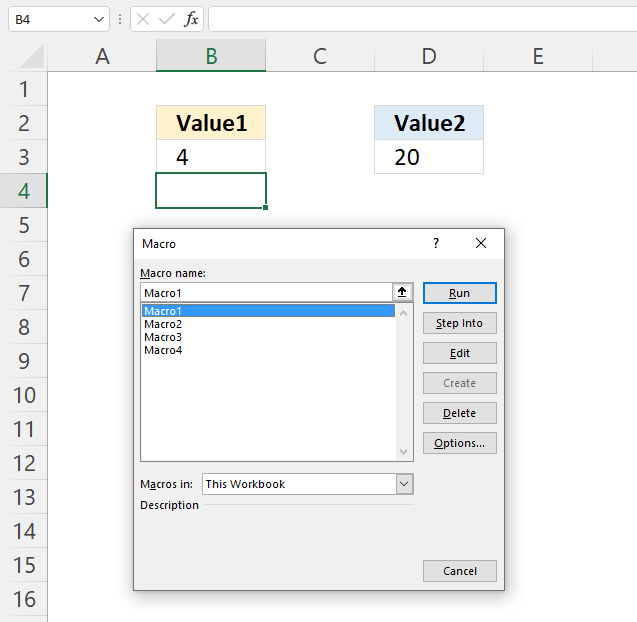
- Press Alt and F8, a dialog box appears.
- Select the macro you want to run.
- Press with left mouse button on "Run" button.
Get Excel *.xlsm macro-enabled file
IF THEN ELSE ENDIF.xlsm
Back to top
Latest updated articles.
More than 300 Excel functions with detailed information including syntax, arguments, return values, and examples for most of the functions used in Excel formulas.
More than 1300 formulas organized in subcategories.
Excel Tables simplifies your work with data, adding or removing data, filtering, totals, sorting, enhance readability using cell formatting, cell references, formulas, and more.
Allows you to filter data based on selected value , a given text, or other criteria. It also lets you filter existing data or move filtered values to a new location.
Lets you control what a user can type into a cell. It allows you to specifiy conditions and show a custom message if entered data is not valid.
Lets the user work more efficiently by showing a list that the user can select a value from. This lets you control what is shown in the list and is faster than typing into a cell.
Lets you name one or more cells, this makes it easier to find cells using the Name box, read and understand formulas containing names instead of cell references.
The Excel Solver is a free add-in that uses objective cells, constraints based on formulas on a worksheet to perform what-if analysis and other decision problems like permutations and combinations.
An Excel feature that lets you visualize data in a graph.
Format cells or cell values based a condition or criteria, there a multiple built-in Conditional Formatting tools you can use or use a custom-made conditional formatting formula.
Lets you quickly summarize vast amounts of data in a very user-friendly way. This powerful Excel feature lets you then analyze, organize and categorize important data efficiently.
VBA stands for Visual Basic for Applications and is a computer programming language developed by Microsoft, it allows you to automate time-consuming tasks and create custom functions.
A program or subroutine built in VBA that anyone can create. Use the macro-recorder to quickly create your own VBA macros.
UDF stands for User Defined Functions and is custom built functions anyone can create.
A list of all published articles.
Source: https://www.get-digital-help.com/how-to-use-the-if-then-else-elseif-end-if-statement-vba/
0 Response to "Vba if Condition Continue Else Exit"
Enregistrer un commentaire